What exactly is RAM, and how does having more of it contribute to boosting the device's performance?
First | What is Random Access Memory (RAM) and its Uses?
As indicated, Random Access Memory is symbolized by the term RAM, which stands for Random Access Memory. This memory stores data in binary form, yet it serves a different purpose than storage. For example, when you install a program on your computer, let's say a drawing software, you will use it multiple times over an extended period. This program and its files are stored in the storage unit.
However, RAM revolves around the present moment. Let's assume you want to draw using a program. Well, what happens? You choose colors, draw lines, adjust the user interface, change settings, select tools, and so on. In other words, you're making rapid changes in real-time. The problem is, you can't access your storage space and make changes to it as swiftly. You need a form of memory that can be altered and influenced at any moment.
This is where Random Access Memory (RAM) comes into play. As its name suggests, it can be accessed randomly. When you open a program, it gets loaded into RAM, reflecting everything you do in real-time. Everything you do within the program affects what's loaded into RAM. This isn't limited to programs; many core functions that keep your device's operating system running are also loaded into RAM. In short, without RAM, your device won't function.
Second| why is more RAM better?
Where's the basement in the subject? Simply put, some devices use a portion of storage space as backup Random Access Memory. The device might have 8 gigabytes of RAM but actually borrow several gigabytes from this storage unit.
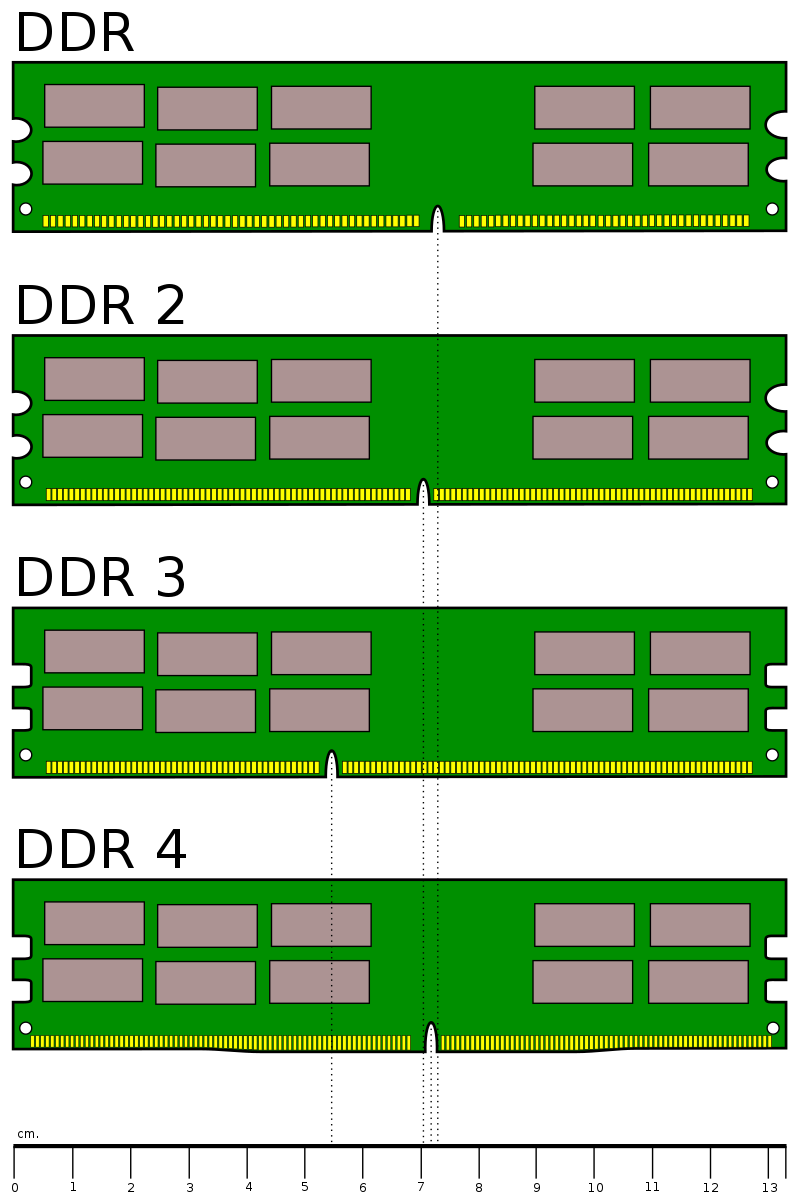
Third | What Does "DDR" Mean?
When you see a new device being released, you might come across the term "DDR." For instance, you might see "16GB of DDR5 RAM," but what does this mean? And why do companies want to impress you with higher DDR numbers?
Technically speaking, DDR uses the same number of pins as SDRAM but operates at a lower voltage (2.5 volts compared to 3.3 volts), reducing power consumption and heat generation. It also uses smaller and lighter memory chips, making it more suitable for mobile devices. DDR operates synchronously, meaning it synchronizes with the CPU clock, which determines the computer's processing speed. This allows DDR to be compatible with CPUs of different frequencies, as long as the DDR speed is equal to or lower than the CPU speed.
Over time, new generations of DDR RAM have emerged, each increasing the speed of RAM. DDR2 doubled the speed of DDR, DDR3 doubled the speed of DDR2, and so on. In terms of numbers, DDR1 operated at around 2.6 volts, while DDR5 operates at 1.1 volts. This means a 56% reduction in power consumption.
Fourth and Finally | What About LPDDR RAM?
LPDDR stands for Low Power Double Data Rate, which is a type of Random Access Memory (RAM) used in mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. LPDDR consumes less power compared to traditional DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM, thereby extending battery life and reducing heat.